ofMesh
An ofMesh represents a set of vertices in 3D spaces, and normals at those points, colors at those points, and texture coordinates at those points. Each of these different properties is stored in a vector. Vertices are passed to your graphics card and your graphics card fill in the spaces in between them in a processing usually called the rendering pipeline. The rendering pipeline goes more or less like this:
-
Say how you're going to connect all the points.
-
Make some points.
-
Say that you're done making points.
You may be thinking: I'll just make eight vertices and voila: a cube. Not so quick. There's a hitch and that hitch is that the OpenGL renderer has different ways of connecting the vertices that you pass to it and none are as efficient as to only need eight vertices to create a cube.
You've probably seen a version of the following image somewhere before.
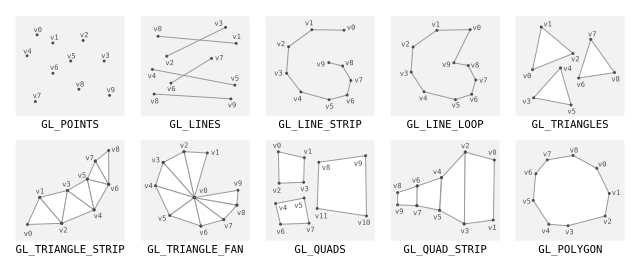
Generally you have to create your points to fit the drawing mode that you've selected because of whats called winding. A vertex gets connected to another vertex in the order that the mode does its winding and this means that you might need multiple vertices in a given location to create the shape you want. The cube, for example, requires eighteen vertices, not the eight that you would expect. If you note the order of vertices in the GL chart above you'll see that all of them use their vertices slightly differently (in particular you should make note of the GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP example). Drawing a shape requires that you keep track of which drawing mode is being used and which order your vertices are declared in.
If you're thinking: it would be nice if there were an abstraction layer for this you're thinking right. Enter the mesh, which is really just an abstraction of the vertex and drawing mode that we started with but which has the added bonus of managing the draw order for you. That may seem insignificant at first, but it provides some real benefits when working with complex geometry.
A very typical usage is something like the following:
ofMesh mesh;
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++){
for (int x = 0; x<width; x++){
mesh.addVertex(ofPoint(x,y,0)); // make a new vertex
mesh.addColor(ofFloatColor(0,0,0)); // add a color at that vertex
}
}
// now it's important to make sure that each vertex is correctly connected with the
// other vertices around it. This is done using indices, which you can set up like so:
for (int y = 0; y<height-1; y++){
for (int x=0; x<width-1; x++){
mesh.addIndex(x+y*width); // 0
mesh.addIndex((x+1)+y*width); // 1
mesh.addIndex(x+(y+1)*width); // 10
mesh.addIndex((x+1)+y*width); // 1
mesh.addIndex((x+1)+(y+1)*width); // 11
mesh.addIndex(x+(y+1)*width); // 10
}
}
addColor( ... )
void addColor(const C &c)This adds a color to the mesh, the color will be associated with the vertex in the same position.
This adds a color to the mesh, the color will be associated with the vertex in the same position.
addColors( ... )
void addColors(const C *cols, size_t amt)This adds a pointer of colors to the ofMesh instance with the amount passed as the second parameter.
This adds a pointer of colors to the ofMesh instance with the amount passed as the second parameter.
addIndex( ... )
void addIndex(ofIndexType i)Will give you this shape:

Add an index to the index vector. Each index represents the order of connection for vertices. This determines the way that the vertices are connected according to the polygon type set in the primitiveMode. It important to note that a particular vertex might be used for several faces and so would be referenced several times in the index vector.
ofMesh mesh;
mesh.setMode(OF_PRIMITIVE_TRIANGLES);
mesh.addVertex(ofPoint(0,-200,0));
mesh.addVertex(ofPoint(200, 0, 0 ));
mesh.addVertex(ofPoint(-200, 0, 0 ));
mesh.addVertex(ofPoint(0, 200, 0 ));
mesh.addIndex(0); //connect the first vertex we made, v0
mesh.addIndex(1); //to v1
mesh.addIndex(2); //to v2 to complete the face
mesh.addIndex(1); //now start a new face beginning with v1
mesh.addIndex(2); //that is connected to v2
mesh.addIndex(3); //and we complete the face with v3
Will give you this shape:
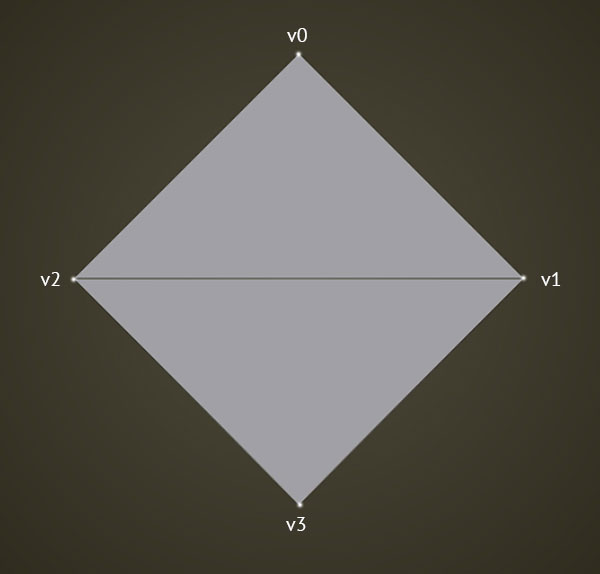
addIndices( ... )
void addIndices(const ofIndexType *inds, size_t amt)This adds indices to the ofMesh by pointing to an array of indices. The "amt" defines the length of the array.
This adds indices to the ofMesh by pointing to an array of indices. The "amt" defines the length of the array.
addNormal( ... )
void addNormal(const N &n)Add a normal to the mesh as a 3D vector, typically perpendicular to the plane of the face. A normal is a vector that defines how a surface responds to lighting, i.e. how it is lit. The amount of light reflected by a surface is proportional to the angle between the light's direction and the normal. The smaller the angle the brighter the surface will look. See the normalsExample for advice on computing the normals. addNormal adds the 3D vector to the end of the list, so you need to make sure you add normals at the same index of the matching vertex.
Add a normal to the mesh as a 3D vector, typically perpendicular to the plane of the face. A normal is a vector that defines how a surface responds to lighting, i.e. how it is lit. The amount of light reflected by a surface is proportional to the angle between the light's direction and the normal. The smaller the angle the brighter the surface will look. See the normalsExample for advice on computing the normals. addNormal adds the 3D vector to the end of the list, so you need to make sure you add normals at the same index of the matching face.
addNormals( ... )
void addNormals(const N *norms, size_t amt)Add an array of normals to the mesh. Because you are using a pointer to the array you also have to define the length of the array as an std::size_t (amt). The normals are added at the end of the current normals list.
Add an array of normals to the mesh. Because you are using a pointer to the array you also have to define the length of the array as an int (amt). The normals are added at the end of the current normals list.
addTexCoord( ... )
void addTexCoord(const T &t)Add a Vec2f representing the texture coordinate. Because OF uses ARB textures these are in pixels rather than 0-1 normalized coordinates.
Add a Vec2f representing the texture coordinate. Because OF uses ARB textures these are in pixels rather than 0-1 normalized coordinates.
addTexCoords( ... )
void addTexCoords(const T *tCoords, size_t amt)Add an array of texture coordinates to the mesh. Because you are using a pointer to the array you also have to define the length of the array as an std::size_t (amt). The texture coordinates are added at the end of the current texture coordinates list.
Add an array of texture coordinates to the mesh. Because you are using a pointer to the array you also have to define the length of the array as an int (amt). The texture coordinates are added at the end of the current texture coordinates list.
addTriangle( ... )
void addTriangle(ofIndexType index1, ofIndexType index2, ofIndexType index3)Adding a triangle means using three of the vertices that have already been added to create a triangle. This is an easy way to create triangles in the mesh. The indices refer to the index of the vertex in the vector of vertices.
Adding a triangle means using three of the vertices that have already been added to create a triangle. This is an easy way to create triangles in the mesh. The indices refer to the index of the vertex in the vector of vertices.
addVertex( ... )
void addVertex(const V &v)Add a new vertex at the end of the current list of vertices. It is important to remember that the order the vertices are added to the list determines how they link they form the polygons and strips (assuming you do not change their indeces). See the ofMesh class description for details.
Add a new vertex at the end of the current list of vertices. It is important to remember that the order the vertices are added to the list determines how they link they form the polygons and strips (assuming you do not change their indeces). See the ofMesh class description for details.
addVertices( ... )
void addVertices(const V *verts, size_t amt)Add an array of vertices to the mesh. Because you are using a pointer to the array you also have to define the length of the array as an int (amt). The vertices are added at the end of the current vertices list.
Add an array of vertices to the mesh. Because you are using a pointer to the array you also have to define the length of the array as an int (amt). The vertices are added at the end of the current vertices list.
clear( )
void clear()Removes all the vertices, colors, and indices from the mesh.
This removes all the vertices, colors, and indices from the mesh.
clearColors( )
void clearColors()Clear all the colors.
Clear all the colors.
clearIndices( )
void clearIndices()Remove all the indices of the mesh. This means that your mesh will be a point cloud.
Remove all the indices of the mesh. This means that your mesh will be a point cloud.
clearNormals( )
void clearNormals()Remove all the normals.
Remove all the normals.
clearTexCoords( )
void clearTexCoords()Clear all the texture coordinates.
Clear all the texture coordinates.
clearVertices( )
void clearVertices()Removes all the vertices.
Removes all the vertices.
disableColors( )
void disableColors()Disable mesh colors. Use enableColors() to turn colors back on.
Disable mesh colors. Use enableColors() to turn colors back on.
disableIndices( )
void disableIndices()Disable mesh indices. Use enableIndices() to turn indices back on.
Disable mesh indices. Use enableIndices() to turn indices back on.
disableNormals( )
void disableNormals()Disable mesh normals. Use enableNormals() to turn normals back on.
Disable mesh normals. Use enableNormals() to turn normals back on.
disableTextures( )
void disableTextures()Disable mesh textures. Use enableTextures() to turn textures back on.
Disable mesh textures. Use enableTextures() to turn textures back on.
draw( )
void draw()This draws the mesh using its primitive type, meaning that if you set them up to be triangles, this will draw the triangles.
This draws the mesh using its primitive type, meaning that if you set them up to be triangles, this will draw the triangles.
draw( ... )
void draw(ofPolyRenderMode renderType)This draws the mesh using a defined renderType, overriding the renderType defined with setMode().
This draws the mesh using a defined renderType, overriding the renderType defined with setMode().
drawFaces( )
void drawFaces()This draws the mesh as faces, meaning that you'll have a collection of faces.
This draws the mesh as faces, meaning that you'll have a collection of faces.
drawVertices( )
void drawVertices()This allows you draw just the vertices, meaning that you'll have a point cloud.
This allows you draw just the vertices, meaning that you'll have a point cloud.
drawWireframe( )
void drawWireframe()This draws the mesh as GL_LINES, meaning that you'll have a wireframe.
This draws the mesh as GL_LINES, meaning that you'll have a wireframe.
enableColors( )
void enableColors()Enable mesh colors. Use disableColors() to turn colors off. Colors are enabled by default when they are added to the mesh.
Enable mesh colors. Use disableColors() to turn colors off. Colors are enabled by default when they are added to the mesh.
enableIndices( )
void enableIndices()Enable mesh indices. Use disableIndices() to turn indices off. Indices are enabled by default when they are added to the mesh.
Enable mesh indices. Use disableIndices() to turn indices off. Indices are enabled by default when they are added to the mesh.
enableNormals( )
void enableNormals()Enable mesh normals. Use disableNormals() to turn normals off. Normals are enabled by default when they are added to the mesh.
Enable mesh normals. Use disableNormals() to turn normals off. Normals are enabled by default when they are added to the mesh.
enableTextures( )
void enableTextures()Enable mesh textures. Use disableTextures() to turn textures off. Textures are enabled by default when they are added to the mesh.
Enable mesh textures. Use disableTextures() to turn textures off. Textures are enabled by default when they are added to the mesh.
flatNormals( )
void flatNormals()Duplicates vertices and updates normals to get a low-poly look.
getCentroid( )
V getCentroid()Returns: a ofVec3f defining the centroid of all the vetices in the mesh.
Returns a ofVec3f defining the centroid of all the vetices in the mesh.
getColor( ... )
C getColor(ofIndexType i)Get the color at the index in the colors vector.
Returns: the color at the index in the colors vector.
Returns the color at the index in the colors vector.
getColorsPointer( )
C * getColorsPointer()Use this if you plan to change the colors as part of this call as it will force a reset of the cache.
Returns: a pointer that contains all of the colors of the mesh, if it has any.
Returns a pointer that contains all of the colors of the mesh, if it has any. Use this if you plan to change the colors as part of this call as it will force a reset of the cache.
getColorsPointer( )
const C * getColorsPointer()Returns: a pointer that contains all of the colors of the mesh, if it has any. (read only)
Returns a pointer that contains all of the colors of the mesh, if it has any. (read only)
getIndex( ... )
ofIndexType getIndex(ofIndexType i)Returns: the index from the index vector. Each index represents the index of the vertex in the vertices vector. This determines the way that the vertices are connected into the polgoynon type set in the primitiveMode.
Returns the index from the index vector. Each index represents the index of the vertex in the vertices vector. This determines the way that the vertices are connected into the polgoynon type set in the primitiveMode.
getIndexPointer( )
ofIndexType * getIndexPointer()Returns: a pointer to the indices that the mesh contains.
Returns a pointer to the indices that the mesh contains.
getIndexPointer( )
const ofIndexType * getIndexPointer()Returns: a pointer to the indices that the mesh contains.
Returns a pointer to the indices that the mesh contains.
getMode( )
ofPrimitiveMode getMode()
Returns: the primitive mode that the mesh is using.
Returns the primitive mode that the mesh is using.
getNormal( ... )
N getNormal(ofIndexType i)
Returns: the normal at the index in the normals vector.
Returns the normal at the index in the normals vector.
getNormalsPointer( )
N * getNormalsPointer()Returns: a pointer to the normals that the mesh contains.
Returns a pointer to the normals that the mesh contains.
getNormalsPointer( )
const N * getNormalsPointer()Returns: a pointer to the normals that the mesh contains.
Returns a pointer to the normals that the mesh contains.
getNumColors( )
size_t getNumColors()Returns: the size of the colors vector for the mesh. This will tell you how many colors are contained in the mesh.
Returns the size of the colors vector for the mesh. This will tell you how many colors are contained in the mesh.
getNumIndices( )
size_t getNumIndices()This will tell you how many indices are contained in the mesh.
Returns: the size of the indices vector for the mesh.
Returns the size of the indices vector for the mesh. This will tell you how many indices are contained in the mesh.
getNumNormals( )
size_t getNumNormals()This will tell you how many normals are contained in the mesh.
Returns: the size of the normals vector for the mesh.
Returns the size of the normals vector for the mesh. This will tell you how many normals are contained in the mesh.
getNumTexCoords( )
size_t getNumTexCoords()This will tell you how many texture coordinates are contained in the mesh.
Returns: the size of the texture coordinates vector for the mesh.
Returns the size of the texture coordinates vector for the mesh. This will tell you how many texture coordinates are contained in the mesh.
getNumVertices( )
size_t getNumVertices()Returns: the size of the vertices vector for the mesh. This will tell you how many vertices are contained in the mesh.
Returns the size of the vertices vector for the mesh. This will tell you how many vertices are contained in the mesh.
getTexCoord( ... )
T getTexCoord(ofIndexType i)Returns: the Vec2f representing the texture coordinate. Because OF uses ARB textures these are in pixels rather than 0-1 normalized coordinates.
Returns the Vec2f representing the texture coordinate. Because OF uses ARB textures these are in pixels rather than 0-1 normalized coordinates.
getTexCoordsPointer( )
T * getTexCoordsPointer()Returns: a pointer to the texture coords that the mesh contains.
Returns a pointer to the texture coords that the mesh contains.
getTexCoordsPointer( )
const T * getTexCoordsPointer()Get a pointer to the ofVec2f texture coordinates that the mesh contains.
Get a pointer to the ofVec2f texture coordinates that the mesh contains.
getVertex( ... )
V getVertex(ofIndexType i)Returns: the vertex at the index.
Returns the vertex at the index.
getVerticesPointer( )
V * getVerticesPointer()Returns: a pointer to the vertices that the mesh contains.
Returns a pointer to the vertices that the mesh contains.
getVerticesPointer( )
const V * getVerticesPointer()Returns: a pointer to the vertices that the mesh contains.
Returns a pointer to the vertices that the mesh contains.
hasColors( )
bool hasColors()/returns Whether the mesh has any colors.
Whether the mesh has any colors.
hasIndices( )
bool hasIndices()/returns Whether the mesh has any indices assigned to it.
Whether the mesh has any indices assigned to it.
hasNormals( )
bool hasNormals()/returnsWhether the mesh has any normals.
Whether the mesh has any normals.
hasTexCoords( )
bool hasTexCoords()/returns Whether the mesh has any textures assigned to it.
Whether the mesh has any textures assigned to it.
hasVertices( )
bool hasVertices()Returns: Whether the mesh has any vertices.
Whether the mesh has any vertices.
haveColorsChanged( )
bool haveColorsChanged()Returns: If the colors of the mesh have changed, been added or removed.
If the colors of the mesh have changed, been added or removed.
haveIndicesChanged( )
bool haveIndicesChanged()Returns: If the indices of the mesh have changed, been added or removed.
If the indices of the mesh have changed, been added or removed.
haveNormalsChanged( )
bool haveNormalsChanged()Returns: If the normals of the mesh have changed, been added or removed.
If the normals of the mesh have changed, been added or removed.
haveTexCoordsChanged( )
bool haveTexCoordsChanged()Returns: If the texture coords of the mesh have changed, been added or removed.
If the texture coords of the mesh have changed, been added or removed.
haveVertsChanged( )
bool haveVertsChanged()Returns: If the vertices of the mesh have changed, been added or removed.
If the vertices of the mesh have changed, been added or removed.
load( ... )
void load(const filesystem::path &path)Loads a mesh from a file located at the provided path into the mesh. This will replace any existing data within the mesh.
It expects that the file will be in the PLY Format. It will only load meshes saved in the PLY ASCII format; the binary format is not supported.
Loads a mesh from a file located at the provided path into the mesh. This will replace any existing data within the mesh.
It expects that the file will be in the PLY Format. It will only load meshes saved in the PLY ASCII format; the binary format is not supported.
mergeDuplicateVertices( )
void mergeDuplicateVertices()ofMesh_( )
ofMesh_()This creates the mesh, using OF_PRIMITIVE_TRIANGLES without any initial vertices.
This creates the mesh, using OF_PRIMITIVE_TRIANGLES and without any initial vertices.
removeColor( ... )
void removeColor(ofIndexType index)Remove a color at the index in the colors vector.
Remove a color at the index in the colors vector.
removeIndex( ... )
void removeIndex(ofIndexType index)Removes an index.
Removes an index.
removeNormal( ... )
void removeNormal(ofIndexType index)Remove a normal.
Remove a normal.
removeTexCoord( ... )
void removeTexCoord(ofIndexType index)Remove a Vec2f representing the texture coordinate.
Remove a Vec2f representing the texture coordinate.
removeVertex( ... )
void removeVertex(ofIndexType index)Removes the vertex at the index in the vector.
Removes the vertex at the index in the vector.
save( ... )
void save(const filesystem::path &path, bool useBinary=false)Saves the mesh at the passed path in the PLY Format.
There are two format options for PLY: a binary format and an ASCII format.
By default, it will save using the ASCII format.
Passing true into the useBinary parameter will save it in the binary format.
If you're planning on reloading the mesh into ofMesh, ofMesh currently only supports loading the ASCII format.
For more information, see the PLY format specification.
Saves the mesh at the passed path in the PLY Format.
There are two format options for PLY: a binary format and an ASCII format.
By default, it will save using the ASCII format.
Passing true into the useBinary parameter will save it in the binary format.
If you're planning on reloading the mesh into ofMesh, ofMesh currently only supports loading the ASCII format.
For more information, see the PLY format specification.
setColor( ... )
void setColor(ofIndexType index, const C &c)Set the color at the index in the colors vector.
Set the color at the index in the colors vector.
setColorForIndices( ... )
void setColorForIndices(ofIndexType startIndex, ofIndexType endIndex, C color)setIndex( ... )
void setIndex(ofIndexType index, ofIndexType val)This sets the index at i.
This sets the index at i.
setMode( ... )
void setMode(ofPrimitiveMode mode)Allows you to set the ofPrimitiveMode. The available modes are OF_PRIMITIVE_TRIANGLES, OF_PRIMITIVE_TRIANGLE_STRIP, OF_PRIMITIVE_TRIANGLE_FAN, OF_PRIMITIVE_LINES, OF_PRIMITIVE_LINE_STRIP, OF_PRIMITIVE_LINE_LOOP, OF_PRIMITIVE_POINTS
Allows you to set the ofPrimitiveMode. The available modes are OF_PRIMITIVE_TRIANGLES, OF_PRIMITIVE_TRIANGLE_STRIP, OF_PRIMITIVE_TRIANGLE_FAN, OF_PRIMITIVE_LINES, OF_PRIMITIVE_LINE_STRIP, OF_PRIMITIVE_LINE_LOOP, OF_PRIMITIVE_POINTS
setNormal( ... )
void setNormal(ofIndexType index, const N &n)\todo Documentation.
setTexCoord( ... )
void setTexCoord(ofIndexType index, const T &t)setVertex( ... )
void setVertex(ofIndexType index, const V &v)setupIndicesAuto( )
void setupIndicesAuto()Allow you to set up the indices automatically when you add a vertex.
Allow you to set up the indices automatically when you add a vertex.
smoothNormals( ... )
void smoothNormals(float angle)usingColors( )
bool usingColors()usingIndices( )
bool usingIndices()usingNormals( )
bool usingNormals()usingTextures( )
bool usingTextures()~ofMesh_( )
~ofMesh_()