ofMatrix4x4
The ofMatrix4x4 is the big class of the math part of openFrameworks. You'll sometimes see it used for doing things like setting where the camera in OepnGL (the mathematically calculated one, not the ofCamera one) is looking or is pointedA, or figuring how to position something in 3d space, doing scaling, etc. The great thing about the 4x4 matrix is that it can do all these things at the same time. A single ofMatrix4x4 can represent a ton of different information about a stuff that goes on in doing 3d programming: where an object is, how you want to scale an object, where a camera is. Let's look at a few really basic examples:
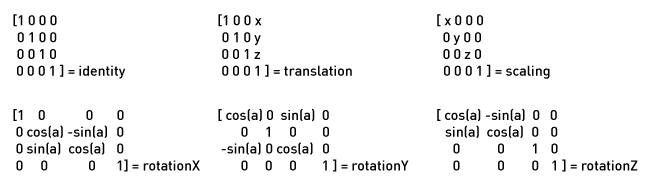
Not particularly exciting, but you can see how they'd be useful. Luckily most of the need to transform, rotate, scale, shear, or further bazzlemunge (just kidding, bazzlemunging is not a thing) stuff in OF is handled internally by objects like ofNode or ofCamera.
decompose( ... )
void decompose(ofVec3f &translation, ofQuaternion &rotation, ofVec3f &scale, ofQuaternion &so)Decompose the matrix into translation, rotation, scale and scale orientation.
getFrustum( ... )
bool getFrustum(double &left, double &right, double &bottom, double &top, double &zNear, double &zFar)Gets the perspective components for a frustum projection matrix.
getInverse( )
ofMatrix4x4 getInverse()Gets the inverse matrix.
getInverseOf( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 getInverseOf(const ofMatrix4x4 &matrix)Makes a new matrix which is the inverse of the given matrix.
getLookAt( ... )
void getLookAt(ofVec3f &eye, ofVec3f ¢er, ofVec3f &up, float lookDistance=1.0f)Gets the lookAt determiners of the matrix.
This function will only work for modelview matrices.
getOrtho( ... )
bool getOrtho(double &left, double &right, double &bottom, double &top, double &zNear, double &zFar)Get the perspective components from a matrix.
This only works with pure perspective projection matrices.
getOrthoNormalOf( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 getOrthoNormalOf(const ofMatrix4x4 &matrix)Makes a new matrix which is the given matrix, normalized.
getPerspective( ... )
bool getPerspective(double &fovy, double &aspectRatio, double &zNear, double &zFar)Get the frustum settings of a symmetric perspective projection matrix.
Note, if matrix is not a symmetric perspective matrix then the shear will be lost. Asymmetric matrices occur when stereo, power walls, caves and reality center display are used. In these configuration one should use the getFrustum method instead.
Returns: false if matrix is not a perspective matrix, where parameter values are undefined.
getPtr( )
float * getPtr()Access the internal data in float* format
useful for opengl matrix transformations
getPtr( )
const float * getPtr()getRotate( )
ofQuaternion getRotate()\name Get Methods {
These return matrix components. getRotate and getScale can only be used if the matrix only has rotation or only has scale, since these transform values are stored in the same area of the matrix. For matrices with both use decompose instead.
getRowAsVec3f( ... )
ofVec3f getRowAsVec3f(size_t i)returns a copy of row i
getRowAsVec4f( ... )
ofVec4f getRowAsVec4f(size_t i)returns a copy of row i
getScale( )
ofVec3f getScale()getTranslation( )
ofVec3f getTranslation()getTransposedOf( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 getTransposedOf(const ofMatrix4x4 &matrix)Makes a new matrix which is the transpose of the given matrix.
glRotate( ... )
void glRotate(const ofQuaternion &q)See also: rotate
glRotate( ... )
void glRotate(float angle, float x, float y, float z)See also: rotate
glRotateRad( ... )
void glRotateRad(float angle, float x, float y, float z)See also: rotate
glScale( ... )
void glScale(const ofVec3f &v)See also: scale
glScale( ... )
void glScale(float x, float y, float z)See also: scale
glTranslate( ... )
void glTranslate(const ofVec3f &v)See also: translate
glTranslate( ... )
void glTranslate(float tx, float ty, float tz)See also: translate
isIdentity( )
bool isIdentity()Checks if the matrix is the identity matrix.
isNaN( )
bool isNaN()Checks if the matrix contains items that are not numbers.
isValid( )
bool isValid()Checks if the matrix is valid by ensuring its items are numbers.
makeFromMultiplicationOf( ... )
void makeFromMultiplicationOf(const ofMatrix4x4 &, const ofMatrix4x4 &)Matrix becomes the result of the multiplication of two other matrices.
makeFrustumMatrix( ... )
void makeFrustumMatrix(double left, double right, double bottom, double top, double zNear, double zFar)Matrix becomes a perspective projection matrix.
Related to: glFrustum. The viewing volume is frustum-shaped and defined by the six parameters. Left, right, top, and bottom specify coordinates in the zNear clipping plane where the frustum edges intersect it, and the zNear and zFar parameters define the forward distances of the view volume. The resulting volume can be vertically and horizontally asymmetrical around the center of the near plane.
makeIdentityMatrix( )
void makeIdentityMatrix()Matrix becomes the identity matrix.
makeInvertOf( ... )
bool makeInvertOf(const ofMatrix4x4 &rhs)Matrix becomes the inverse of the provided matrix.
makeLookAtMatrix( ... )
void makeLookAtMatrix(const ofVec3f &eye, const ofVec3f ¢er, const ofVec3f &up)Matrix becomes a combination of translation and rotation.
Matrix becomes a combination of a translation to the position of 'eye' and a rotation matrix which orients an object to point towards 'center' along its z-axis. Use this function if you want an object to look at a point from another point in space.
Parameters:
eye The position of the object.
center The point which the object is "looking" at.
up The direction which the object considers to be "up".
makeLookAtViewMatrix( ... )
void makeLookAtViewMatrix(const ofVec3f &eye, const ofVec3f ¢er, const ofVec3f &up)Matrix becomes a combination of an inverse translation and rotation.
Related to: gluLookAt. This creates the inverse of makeLookAtMatrix. The matrix will be an opposite translation from the 'eye' position, and it will rotate things in the opposite direction of the eye-to-center orientation. This is definitely confusing, but the main reason to use this transform is to set up a view matrix for a camera that's looking at a certain point. To achieve the effect of moving the camera somewhere and rotating it so that it points at something, the rest of the world is moved in the opposite direction and rotated in the opposite way around the camera. This way, you get the same effect as moving the actual camera, but all the projection math can still be done with the camera positioned at the origin (which makes it way simpler).
makeOrtho2DMatrix( ... )
void makeOrtho2DMatrix(double left, double right, double bottom, double top)Matrix becomes a 2D orthographic projection matrix.
Related to: glOrtho2D. The box-shaped viewing volume is described by the four parameters and, implicitly, a zNear of -1 and a zFar of 1.
makeOrthoMatrix( ... )
void makeOrthoMatrix(double left, double right, double bottom, double top, double zNear, double zFar)Matrix becomes an orthographic projection matrix.
Related to: glOrtho. The orthographic projection has a box-shaped viewing volume described by the six parameters. Left, right, bottom, and top specify coordinates in the zNear clipping plane where the corresponding box sides intersect it.
makeOrthoNormalOf( ... )
void makeOrthoNormalOf(const ofMatrix4x4 &rhs)Matrix becomes an orthonormalized version of the provided matrix.
The basis vectors (the 3x3 chunk embedded in the upper left of the matrix) are normalized. This means the resulting matrix has had scaling effects removed. The fourth column and the fourth row are transferred over untouched, so translation will be included as well.
makePerspectiveMatrix( ... )
void makePerspectiveMatrix(double fovy, double aspectRatio, double zNear, double zFar)Matrix becomes a perspective projection matrix.
Related to: gluPerspective. The viewing volume is frustum-shaped amd defined by the four parameters. The fovy and aspect ratio are used to compute the positions of the left, right, top, and bottom sides of the viewing volume in the zNear plane. The fovy is the y field-of-view, the angle made by the top and bottom sides of frustum if they were to intersect. The aspect ratio is the width of the frustum divided by its height. Note that the resulting volume is both vertically and horizontally symmetrical around the center of the near plane.
makeRotationMatrix( ... )
void makeRotationMatrix(const ofVec3f &from, const ofVec3f &to)\name Rotation { Matrix becomes a rotation transform.
Parameters:
from Matrix becomes a rotation from this vector direction.
to Matrix becomes a rotation to this vector direction.
makeRotationMatrix( ... )
void makeRotationMatrix(const ofQuaternion &quaternion)Parameters:
quaternion Matrix becomes a rotation that produces the quaternion's orientation.
makeRotationMatrix( ... )
void makeRotationMatrix(float angle, const ofVec3f &axis)Parameters:
angle Matrix becomes a rotation by angle (degrees).
axis Rotation is performed around this vector.
makeRotationMatrix( ... )
void makeRotationMatrix(float angle, float x, float y, float z)Parameters:
angle Matrix becomes a rotation by angle (degrees).
x X-value of the rotation axis.
y Y-value of the rotation axis.
z Z-value of the rotation axis.
makeRotationMatrix( ... )
void makeRotationMatrix(float angle1, const ofVec3f &axis1, float angle2, const ofVec3f &axis2, float angle3, const ofVec3f &axis3)Matrix becomes a rotation around multiple axes.
The final rotation is the result of rotating around each of the three axes, in order. Angles are given in degrees, and axes can be arbitrary vectors.
makeScaleMatrix( ... )
void makeScaleMatrix(const ofVec3f &)\name Scale { Matrix becomes a scale transform.
Accepts x, y, z scale values as a vector or separately.
makeScaleMatrix( ... )
void makeScaleMatrix(float , float , float )makeTranslationMatrix( ... )
void makeTranslationMatrix(const ofVec3f &)\name Translation { Matrix becomes a translation transform.
Accepts x, y, z translation values as a vector or separately.
makeTranslationMatrix( ... )
void makeTranslationMatrix(float , float , float )newFrustumMatrix( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 newFrustumMatrix(double left, double right, double bottom, double top, double zNear, double zFar)See also: makeFrustumMatrix
newIdentityMatrix( )
ofMatrix4x4 newIdentityMatrix()See also: makeIdentityMatrix
newLookAtMatrix( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 newLookAtMatrix(const ofVec3f &eye, const ofVec3f ¢er, const ofVec3f &up)See also: makeLookAtMatrix
newOrtho2DMatrix( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 newOrtho2DMatrix(double left, double right, double bottom, double top)See also: makeOrtho2DMatrix
newOrthoMatrix( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 newOrthoMatrix(double left, double right, double bottom, double top, double zNear, double zFar)See also: makeOrthoMatrix
newPerspectiveMatrix( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 newPerspectiveMatrix(double fovy, double aspectRatio, double zNear, double zFar)See also: makePerspectiveMatrix
newRotationMatrix( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 newRotationMatrix(const ofVec3f &from, const ofVec3f &to)See also: makeRotationMatrix
newRotationMatrix( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 newRotationMatrix(const ofQuaternion &quat)newRotationMatrix( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 newRotationMatrix(float angle, const ofVec3f &axis)newRotationMatrix( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 newRotationMatrix(float angle, float x, float y, float z)newRotationMatrix( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 newRotationMatrix(float angle1, const ofVec3f &axis1, float angle2, const ofVec3f &axis2, float angle3, const ofVec3f &axis3)newScaleMatrix( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 newScaleMatrix(const ofVec3f &sv)See also: makeScaleMatrix
newScaleMatrix( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 newScaleMatrix(float sx, float sy, float sz)newTranslationMatrix( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 newTranslationMatrix(const ofVec3f &dv)See also: makeTranslationMatrix
newTranslationMatrix( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 newTranslationMatrix(float x, float y, float z)ofMatrix4x4( ... )
ofMatrix4x4(const glm::mat4 &mat)ofMatrix4x4( ... )
ofMatrix4x4(const ofQuaternion &quat)Rotation matrices can be constructed from a quaternion.
ofMatrix4x4( )
ofMatrix4x4()The default constructor provides an identity matrix.
ofMatrix4x4( ... )
ofMatrix4x4(float a00, float a01, float a02, float a03, float a10, float a11, float a12, float a13, float a20, float a21, float a22, float a23, float a30, float a31, float a32, float a33)Positional style.
All 16 values of the matrix as positional arguments in row-major order.
ofMatrix4x4( ... )
ofMatrix4x4(const float *const ptr)Construct with a pointer.
You can pass a pointer to floats, and the first 16 contents will be extracted into this matrix.
Warning: the validity of these values is not checked!
operator()( ... )
float & operator()(size_t row, size_t col)Write data with matrix(row,col)=number
operator()( ... )
float operator()(size_t row, size_t col)Read data with matrix(row, col)
operator*( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 operator*(const ofMatrix4x4 &m)creates a new matrix from the product of two matrices.
operator*( ... )
ofVec3f operator*(const ofVec3f &v)Matrix * Vector operator.
Calls postMult() internally.
operator*( ... )
ofVec4f operator*(const ofVec4f &v)operator*=( ... )
void operator*=(const ofMatrix4x4 &other)The *= operation for matrices.
This is equivalent to calling postMult(other), but it allows you to do someMatrix *= someMatrix without breaking const-correctness. Calling someMatrix.postMult(someMatrix) won't work.
operator=( ... )
ofMatrix4x4 & operator=(const ofMatrix4x4 &rhs)Copy a matrix using = operator.
postMult( ... )
void postMult(const ofMatrix4x4 &)Post-multiply by another matrix.
This matrix becomes this * other.
postMult( ... )
ofVec3f postMult(const ofVec3f &v)Matrix * vector multiplication.
This operation implicitly treat vectors as column-matrices.
postMult( ... )
ofVec4f postMult(const ofVec4f &v)post-multiplies the vector by the matrix (i.e. returns M mult v). The vector is implicitly treated as a column-matrix
postMultRotate( ... )
void postMultRotate(const ofQuaternion &q)Equivalent to postMult(newRotationMatrix(q)).
postMultRotate( ... )
void postMultRotate(float angle, float x, float y, float z)postMultScale( ... )
void postMultScale(const ofVec3f &v)Equivalent to postMult(scale(v)).
postMultScale( ... )
void postMultScale(float x, float y, float z)postMultTranslate( ... )
void postMultTranslate(const ofVec3f &v)Equivalent to postMult(newTranslationMatrix(v)).
postMultTranslate( ... )
void postMultTranslate(float x, float y, float z)the positional argument version of the above
preMult( ... )
void preMult(const ofMatrix4x4 &)Pre-multiply by another matrix.
This matrix becomes other * this.
preMult( ... )
ofVec3f preMult(const ofVec3f &v)Vector * matrix multiplication.
This operation implicitly treats vectors as row-matrices.
preMult( ... )
ofVec4f preMult(const ofVec4f &v)pre-multiplies the vector by the matrix (i.e. returns v mult M) The vector is implicitly treated as a row-matrix
preMultRotate( ... )
void preMultRotate(const ofQuaternion &q)Equivalent to preMult(newRotationMatrix(q)).
preMultScale( ... )
void preMultScale(const ofVec3f &v)Equivalent to preMult(newScaleMatrix(v)).
preMultTranslate( ... )
void preMultTranslate(const ofVec3f &v)Equivalent to preMult(newTranslationMatrix(v)).
rotate( ... )
void rotate(const ofQuaternion &q)Rotates based on the quarternion.
rotate( ... )
void rotate(float angle, float x, float y, float z)Rotates by angle (degrees) around the given x, y, z axis.
rotateRad( ... )
void rotateRad(float angle, float x, float y, float z)Rotates by angle (radians) around the given x, y, z axis.
scale( ... )
void scale(const ofVec3f &v)Scales each axis by the corresponding x, y, z of the vector.
scale( ... )
void scale(float x, float y, float z)Scales each axis by the corresponding x, y, z.
set( ... )
void set(const ofMatrix4x4 &rhs)Set the data of the matrix.
These functions are analogous to the corresponding constructors.
set( ... )
void set(float a00, float a01, float a02, float a03, float a10, float a11, float a12, float a13, float a20, float a21, float a22, float a23, float a30, float a31, float a32, float a33)set( ... )
void set(const float *const ptr)set( ... )
void set(const double *const ptr)setRotate( ... )
void setRotate(const ofQuaternion &q)\name Set methods {
All of these methods alter the components, deleting the previous data only in that component.
setTranslation( ... )
void setTranslation(const ofVec3f &v)setTranslation( ... )
void setTranslation(float tx, float ty, float tz)transform3x3( ... )
ofVec3f transform3x3(const ofMatrix4x4 &m, const ofVec3f &v)Apply a 3x3 transform (no translation) of M * v.
transform3x3( ... )
ofVec3f transform3x3(const ofVec3f &v, const ofMatrix4x4 &m)Apply a 3x3 transform (no translation) of v * M.
translate( ... )
void translate(const ofVec3f &v)Translates along the vector.
translate( ... )
void translate(float tx, float ty, float tz)Translates by tx, ty, tz.
~ofMatrix4x4( )
~ofMatrix4x4()destructor.